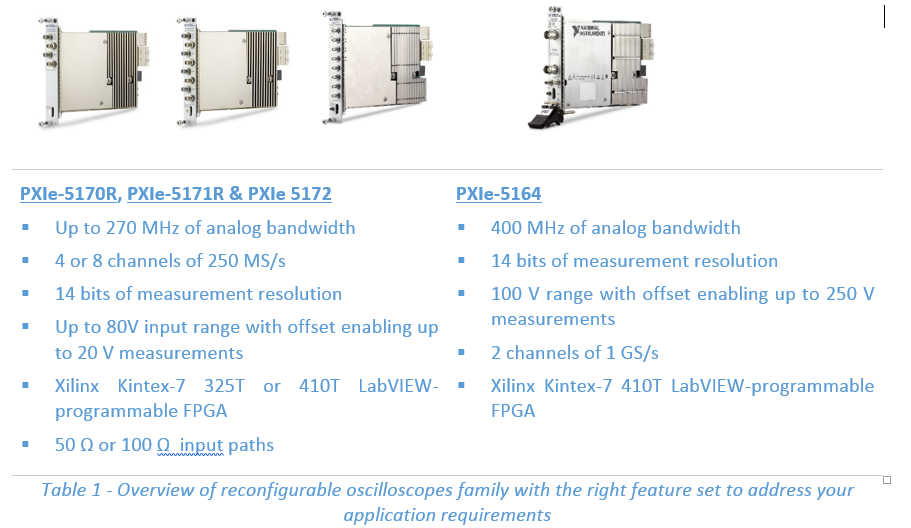
In recent years, however, user-configurable FPGA instrumentation offerings have become more advanced and “instrument-like.” NI offers variety of modular instruments with user-programmable FPGAs for example, the reconfigurable oscilloscope family features devices with up to 400 MHz of analog bandwidth, eight input channels on a single slot PXI module, 14 bits of measurement resolution, 1 GS/s sampling rate, and a user-programmable Xilinx Kintex-7 FPGA. The NI PXI vector signal transceiver is a reconfigurable I/O (RIO) instrument that integrates an RF vector signal generator, an RF signal analyzer, baseband I/O, digital I/O, and a user-configurable FPGA onto the same module.
In 2012, when the vector signal transceiver (VST) was first introduced, it offered an open source instrument driver experience. From capturing IQ samples to timing and triggering, one could modify and customize the implementation of the instrument driver itself. The VST is essence, provides a blank canvas for the test system designer to use LabVIEW FPGA to implement a custom RF instrument. To serve users yearning for something that mimicked a traditional instrument driver, NI augmented the VST software experience by allowing engineers to program the device using standard instrument drivers such as the NI-RFSA and NI-RFSG drivers. The VST architecture enables a variety of application-specific enhancements that take advantage of the parallelism, low-latency control, and processing performance of the FPGA.