Electrical power grids have recently embraced digital transformation, driven by the pursuit of net-zero carbon emissions. This evolution has turned legacy utility networks into smart grids, aiming to enhance energy management through real-time data collection and analysis. Ensuring the smooth operation of a smart grid is a complex task, necessitating effective solutions for timely data acquisition, analysis, and notifications among diverse subsystems.
Navigating the Intricacies of Smart Grids
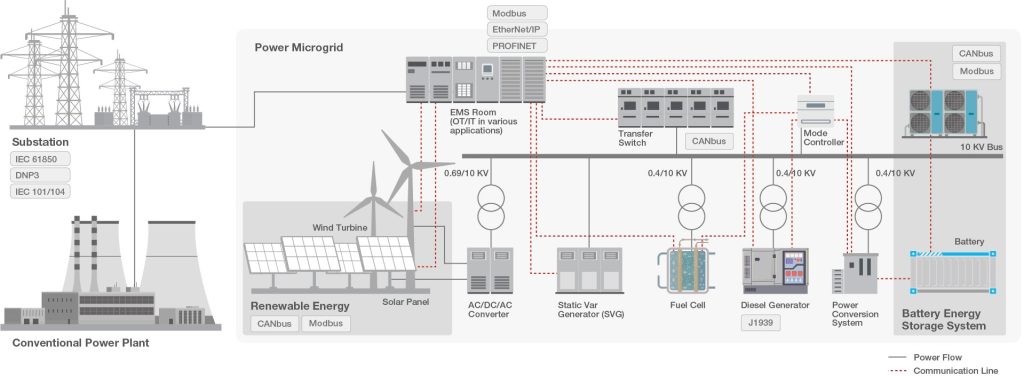
Smart grids encompass multiple subsystems, including traditional power generation, renewable energy sources, digital substations, microgrids, energy storage systems, and end users. Each subsystem has unique characteristics and requirements, such as power distribution control, power monitoring, and energy storage management. The challenge lies in the diverse communication protocols used by these subsystems. For example, feeder lines typically use IEC 61850, DNP3, or IEC 101/104; meters rely on Modbus; renewable energy systems use CANbus; and backup power systems employ J1939. Integrating all this data is a complex task.
Challenges and Solutions
Effective protocol conversion and data integration are critical in this complex environment. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) are often used for this purpose, but they require extensive programming, which increases both cost and complexity. Industrial computers are another option, but they demand expertise in managing various communication protocols. Additionally, on-site diagnostic and troubleshooting tools are necessary to address potential issues even after the system has been operational for some time. The complex network topology also requires careful consideration of network security, especially in harsh environments.
Protocol gateways provide an optimal solution. They enable protocol conversion through simple configuration, eliminating the need for extensive programming. This facilitates seamless data integration and communication between different systems, even without extensive technical skills.
Streamlining Remote Troubleshooting for Smart Grid Devices
Many smart grid devices are located in remote areas, making remote access and troubleshooting essential to minimize the time and cost associated with dispatching personnel for on-site issue resolution. Protocol gateways offer built-in tools for troubleshooting, significantly reducing the time required for fault diagnosis and the cost of external debugging tools.
Ensuring Security in Smart Grids
Given the potential for remote connections to protocol gateways, security is paramount. Protocol gateways need to provide secure connection features, such as HTTPS connections, robust account and password management, and comprehensive event log recordings. These features help mitigate the risk of hacker attacks and ensure system security.
Ensuring Reliability in Harsh Conditions
Smart grid equipment often operates in harsh environments. Therefore, protocol gateways must be rugged, with resistance to wide temperature ranges and electromagnetic interference, to ensure the system’s overall reliability.
Conclusion
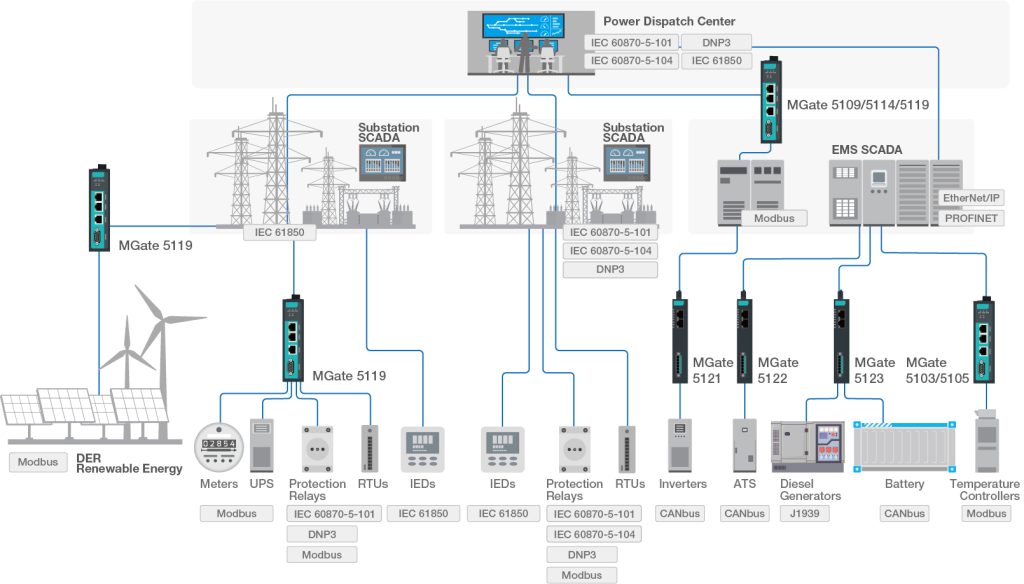
In the smart grid era, protocol gateways are crucial for ensuring smooth data flow between different systems. The various communication protocols used by the subsystems of the electrical grid require effective protocol conversion and seamless data communication to fully realize a smart grid. Protocol gateways enable easy protocol conversion through simple configuration, remote troubleshooting, and enhanced system security. Implementing this technology will contribute to smarter and more efficient energy management, advancing the development of smart grids and transforming electricity delivery worldwide.
Story credit: Moxa








