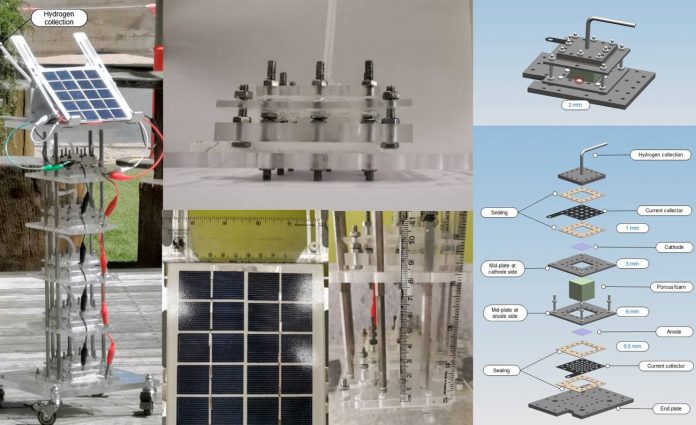
A team of researchers at the University of Melbourne, working with a colleague from the University of Manchester, has developed a device that can use humidity from the air to make hydrogen gas the group describes their device and its performance under lab conditions.
As scientists around the world seek solutions to reduce global warming, many have focused on the production of hydrogen gas as a replacement energy source. It is a zero-carbon fuel that yields only water as a byproduct when combusted. Hydrogen gas is typically made by splitting water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen, a process called electrolysis. It is carried out by passing an electric current through a sample of water. This starts a chemical reaction that leads to the decomposition of the materials in the molecule.
Most efforts to use electrolysis involve water from a pure source and tend to be complicated and expensive, which is why hydrogen is still not widely used to power vehicles. In this new effort, the researchers simplified the process and used a readily available source of water—humidity.
The device, which the team calls a direct air electrolysis module, was made using sponge-like materials for the electrodes. They liken them to silica gel often seen in moisture absorption packets. The moisture that is gathered moves to a chamber where it is electrolyzed. The key to the success of the module was that the hygroscopic electrolytes can be exposed to the atmosphere all the time.
The electricity to power the reactions was obtained from an easily available renewable resource—a small wind turbine. As positively charged electrodes moved through the water, electrons were pulled from the molecules, resulting in the formation of positively charged oxygen ions and negatively charged hydrogen ions. The oxygen was released and the hydrogen was captured.
The prototype was able to produce hydrogen for more than 12 consecutive days. The researchers also let it run by itself for eight months to determine its durability. And they found that it worked with humidity levels as low as 4%. Testing thus far has shown the device to be capable of producing enough hydrogen to heat a home. They also note that while the prototype is small, it could be scaled up or multiple modules could be connected together.