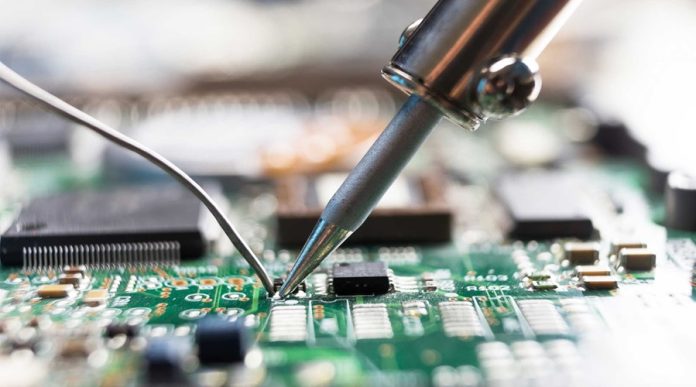
Soldering is a process used to join two or more metal components by melting and flowing a filler metal, known as solder, into the joint. The filler metal has a lower melting point than the workpieces, ensuring that the base materials do not melt during the process. Soldering is widely used in electronics, plumbing, jewellery making, and metalwork due to its ability to create reliable and conductive joints.
Soldering History
The history of soldering dates back thousands of years to ancient civilizations. The earliest evidence of soldering was found in Mesopotamia around 3000 BCE, where goldsmiths used soldering to join gold pieces. Ancient Egyptians and Romans also used soldering techniques for jewellery and weaponry. By the Middle Ages, soldering became essential in stained glass art and decorative metalwork. The industrial revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries saw significant advancements in soldering tools and materials, making it integral to electrical and mechanical applications. Today, soldering remains a cornerstone in modern manufacturing and repair processes.
Types of Soldering
Soldering techniques are categorized based on the temperature and materials involved:
- Soft Soldering:
- Operates at temperatures below 400°C (752°F).
- Commonly used in electronics and plumbing.
- Utilizes tin-lead or lead-free alloys.
- Hard Soldering:
- Involves higher temperatures and stronger joints.
- Includes techniques like silver soldering.
- Used in jewellery, metalwork, and mechanical assemblies.
- Brazing:
- Often considered a high-temperature form of soldering.
- Filler metals like brass or silver are melted above 450°C (842°F).
- Suitable for heavy-duty applications, including aerospace and automotive industries.
- Wave Soldering:
- Used in mass production of printed circuit boards (PCBs).
- Components are soldered simultaneously by passing them over a wave of molten solder.
- Reflow Soldering:
- Involves applying solder paste and heating it to attach electronic components.
- Widely used in surface-mount technology (SMT).
How Does Soldering Work?
Soldering works by creating a metallurgical bond between the solder and the base materials. The process involves:
- Preparation: The surfaces to be joined are cleaned to remove oxidation, dirt, and grease.
- Flux Application: Flux is applied to prevent oxidation during heating and to improve solder flow.
- Heating: A soldering iron or other heat source heats the joint, melting the solder.
- Bond Formation: The molten solder flows into the joint via capillary action and solidifies, forming a strong, conductive bond.
The Soldering Process
- Clean the Components: Ensure the surfaces are free of contaminants for a strong bond.
- Apply Flux: Spread flux on the joint area to enhance adhesion and prevent oxidation.
- Heat the Joint: Use a soldering iron to heat the connection point, not the solder directly.
- Apply Solder: Feed the solder wire into the heated joint, allowing it to flow naturally.
- Inspect the Joint: Check for a shiny and smooth appearance, indicating a successful bond.
- Clean the Joint: Remove any residual flux or debris for a neat finish.
Soldering Uses & Applications
Soldering is employed across various industries for diverse applications:
- Electronics:
- Assembling circuit boards.
- Repairing electronic devices like smartphones, TVs, and laptops.
- Plumbing:
- Joining copper pipes for water supply and HVAC systems.
- Jewellery Making:
- Creating intricate designs and securing precious stones.
- Automotive:
- Connecting wiring harnesses and electronic components in vehicles.
- Art and Craft:
- Stained glass creation and decorative metal projects.
- Aerospace and Defense:
- Ensuring reliable connections in high-performance environments.
Soldering Advantages
- Strong Joints: Produces durable connections capable of withstanding mechanical stress.
- Electrical Conductivity: Ensures reliable electrical connections in circuits.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of materials and industries.
- Cost-Effective: Requires relatively inexpensive tools and materials.
- Repairability: Allows for easy rework and repairs of damaged joints.
- Precision: Enables intricate and delicate work, especially in electronics and jewelry.
Soldering Machine
Soldering machines are automated or semi-automated tools designed to enhance the soldering process. They are used for efficiency and precision in industrial applications. Common types include:
- Soldering Irons: Handheld tools with a heated tip for manual soldering.
- Soldering Stations: Advanced setups with adjustable temperature controls and interchangeable tips.
- Wave Soldering Machines: Automate the soldering of components on PCBs for high-volume production.
- Reflow Soldering Ovens: Heat solder paste to attach surface-mounted components in electronic assemblies.
- Robotic Soldering Machines: Use programmed movements for consistent and precise soldering in manufacturing.
Conclusion
Soldering is a fundamental technique that has evolved significantly over centuries, finding applications across industries due to its reliability and efficiency. From ancient goldsmiths to modern electronics, soldering continues to enable the creation and repair of essential components in our daily lives. With advancements in soldering tools and machines, it remains a vital process in manufacturing, art, and engineering, driving innovation and connectivity worldwide.