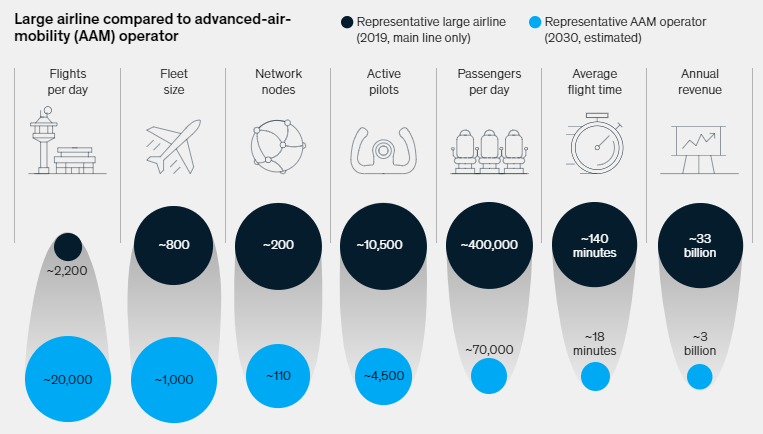
With projections indicating a doubling of air passenger numbers to 8.2 million by 2037, the advancement of all-electric and hybrid-electric propulsion for powering Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) is evolving into a billion-dollar industry. Recent assessments by Rolls Royce suggest that approximately 15,000 Electric Vertical Take-Off and Landing (eVTOL) vehicles will be indispensable across 30 major cities by 2035 solely to meet the demand for intracity travel. By 2030, top players in the passenger Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) sector could boast larger fleets and significantly more daily flights than the world’s biggest airlines. These flights, averaging just 18 minutes each, will typically carry fewer passengers (ranging from one to six, plus a pilot).
The increasing urbanization, expanding population, aging infrastructure, and the surge in e-commerce and logistics underscore the need for a contemporary, safe, and cost-effective transportation solution for both people and goods. Urban Air Mobility (UAM) presents a seamless, reliable, and swift mode of transportation, addressing present and future urban challenges. With the capacity to transform intra and inter-city transportation, UAM offers a quicker and more effective alternative to conventional ground-based transportation methods. The adoption of Urban Air Mobility hinges on five primary factors:
- Growing demand for alternate modes of transportation in urban mobility.
- Need for convenient, efficient and last mile delivery.
- Zero emission and noise free mandates.
- Advancement in technologies (Energy storage, Autonomous, Connected, Power Electronics).
- Security.
Despite the growing Urban Air Mobility (UAM) sector, it faces significant challenges that need addressing for future growth and success. These challenges range from developing reliable electric propulsion systems to achieving autonomous flight capabilities and establishing necessary infrastructure like vertiports and charging stations. Overcoming these hurdles is vital for unlocking UAM’s transformative potential in urban transportation.
AI Integration for UAM Enhancement
Utilizing AI for predictive maintenance enables analysis of sensor data and onboard sources to forecast maintenance needs, reducing downtime and increasing aircraft availability. AI-enabled maintenance inspections allow for rapid issue identification through image analysis of eVTOLs and UAVs, minimizing errors and oversights. AI aids in making better decisions for aircraft maintenance support by thoroughly analyzing various considerations, likely leading to improved outcomes. Additionally, robotic systems equipped with AI algorithms can autonomously repair or replace minor parts, enhancing safety for maintenance teams. Moreover, AI facilitates better diagnostics and targeted troubleshooting, expediting issue identification and repair suggestions. Ultimately, proactive maintenance, data integration, and improved safety are promised by AI in UAM, ensuring aircraft are maintained effectively from takeoff to landing.
AI in Intelligent Cabin Management (ICMS)
The Intelligent Cabin Management System (ICMS), utilized in aviation and rail industries, undergoes continuous advancements fueled by emerging technologies. Enhanced facial recognition algorithms, driven by artificial intelligence (AI), significantly improve efficiencies and reliability in user authentication, behavior analysis, safety, threat detection, and object tracking. Moreover, ICMS prioritizes monitoring passengers’ vital signs onboard for health safety.
This solution ensures cabin operations with a focus on passenger safety, security, and health, suitable for various passenger cabins in aircraft and rail, and particularly ideal for UAM applications. It facilitates cabin entry by authorized crew and passengers, guides seating arrangements, enforces luggage placement regulations, ensures compliance with air travel advisories, monitors passenger behavior for preemptive intervention, identifies permitted and potentially threatening objects, flags left luggage, and detects vital health parameters for real-time monitoring and control.
AI in UAM Maintenance
AI-driven predictive maintenance involves analyzing sensor data and onboard sources to anticipate UAM maintenance needs, aiding in proactive scheduling and minimizing downtime. Similarly, AI-based inspections utilize image analysis to swiftly identify potential issues during regular checks, enhancing accuracy and reducing errors. Additionally, AI supports maintenance decision-making by analyzing various factors like repair costs and part availability, providing informed recommendations. Future advancements may see autonomous maintenance systems, powered by AI, performing routine tasks such as inspections and minor repairs, improving efficiency and safety. Furthermore, AI assists technicians in diagnostics and troubleshooting by analyzing data and historical records to pinpoint issues and suggest appropriate solutions, streamlining maintenance processes and ensuring UAM operational reliability.
Conclusion
The integration of AI into UAM maintenance offers numerous benefits that significantly enhance the efficiency, safety, and reliability of UAM operations. Through proactive maintenance enabled by AI’s predictive capabilities, maintenance teams can anticipate and address potential failures before they occur, reducing unplanned downtime and enhancing operational reliability. Furthermore, AI-supported maintenance increases aircraft availability, ensuring vehicles are consistently safe and reliable, thus contributing to higher customer satisfaction and overall operational performance.
Moreover, AI-driven maintenance optimization leads to cost reduction by accurately predicting maintenance needs and minimizing unnecessary inspections and component replacements, thereby reducing labor and material costs. Additionally, AI’s continuous monitoring of UAM vehicle conditions enhances safety by detecting anomalies or safety risks in real-time, preventing accidents and ensuring timely maintenance. Overall, the application of AI in UAM maintenance represents a transformative step towards a more efficient, safe, and reliable urban air transportation system.